Polymyositis
What is Polymyositis?
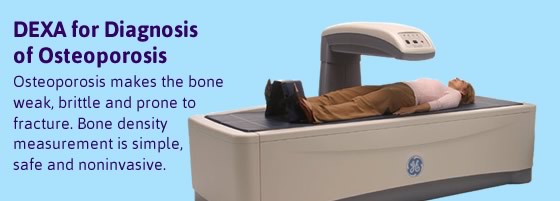
Polymyositis is one of a group of muscle diseases known as the inflammatory myopathies, which are characterized by chronic muscle inflammation accompanied by muscle weakness. Polymyositis affects skeletal muscles (those involved with making movement) on both sides of the body. It is rarely seen in persons under age 18; most cases are in adults between the ages of 31 and 60. Progressive muscle weakness starts in the proximal muscles (muscles closest to the trunk of the body) which eventually leads to difficulties climbing stairs, rising from a seated position, lifting objects, or reaching overhead. People with polymyositis may also experience arthritis, shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing and speaking, and heart arrhythmias. In some cases of polymyositis, distal muscles (muscles further away from the trunk of the body, such as those in the forearms and around the ankles and wrists) may be affected as the disease progresses. Polymyositis may be associated with collagen-vascular or autoimmune diseases, such as lupus. Polymyositis may also be associated with infectious disorders, such as HIV-AIDS.
What causes polymyositis?
To date, no cause of polymyositis has been isolated by scientific researchers. There are indicators of heredity (genetic) susceptibility that can be found in some patients. There is indirect evidence of infection by a virus that has yet to be identified in a muscle disease related to polymyositis that is particularly resistant to treatment, called inclusion body myositis.
Is there any treatment?
There is no cure for polymyositis, but the symptoms can be treated. Options include medication, physical therapy, exercise, heat therapy (including microwave and ultrasound), orthotics and assistive devices, and rest. The standard treatment for polymyositis is a corticosteroid drug, given either in pill form or intravenously. Immunosuppressant drugs, such as azathioprine and methotrexate, may reduce inflammation in people who do not respond well to prednisone. Periodic treatment using intravenous immunoglobulin can also improve recovery. Other immunosuppressive agents used to treat the inflammation associated with polymyositis include cyclosporine A, cyclophosphamide, and tacrolimus. Physical therapy is usually recommended to prevent muscle atrophy and to regain muscle strength and range of motion.
What is the prognosis?
The prognosis for polymyositis varies. Most people respond fairly well to therapy, but some have a more severe disease that does not respond adequately to therapies and are left with significant disability. In rare cases individuals with severe and progressive muscle weakness will develop respiratory failure or pneumonia. Difficulty swallowing may cause weight loss and malnutrition.
 Riverside6180 Brockton Avenue, Riverside, CA 92506
Riverside6180 Brockton Avenue, Riverside, CA 92506 La Sierra4244 Riverwalk Parkway, Riverside, CA 92505
La Sierra4244 Riverwalk Parkway, Riverside, CA 92505